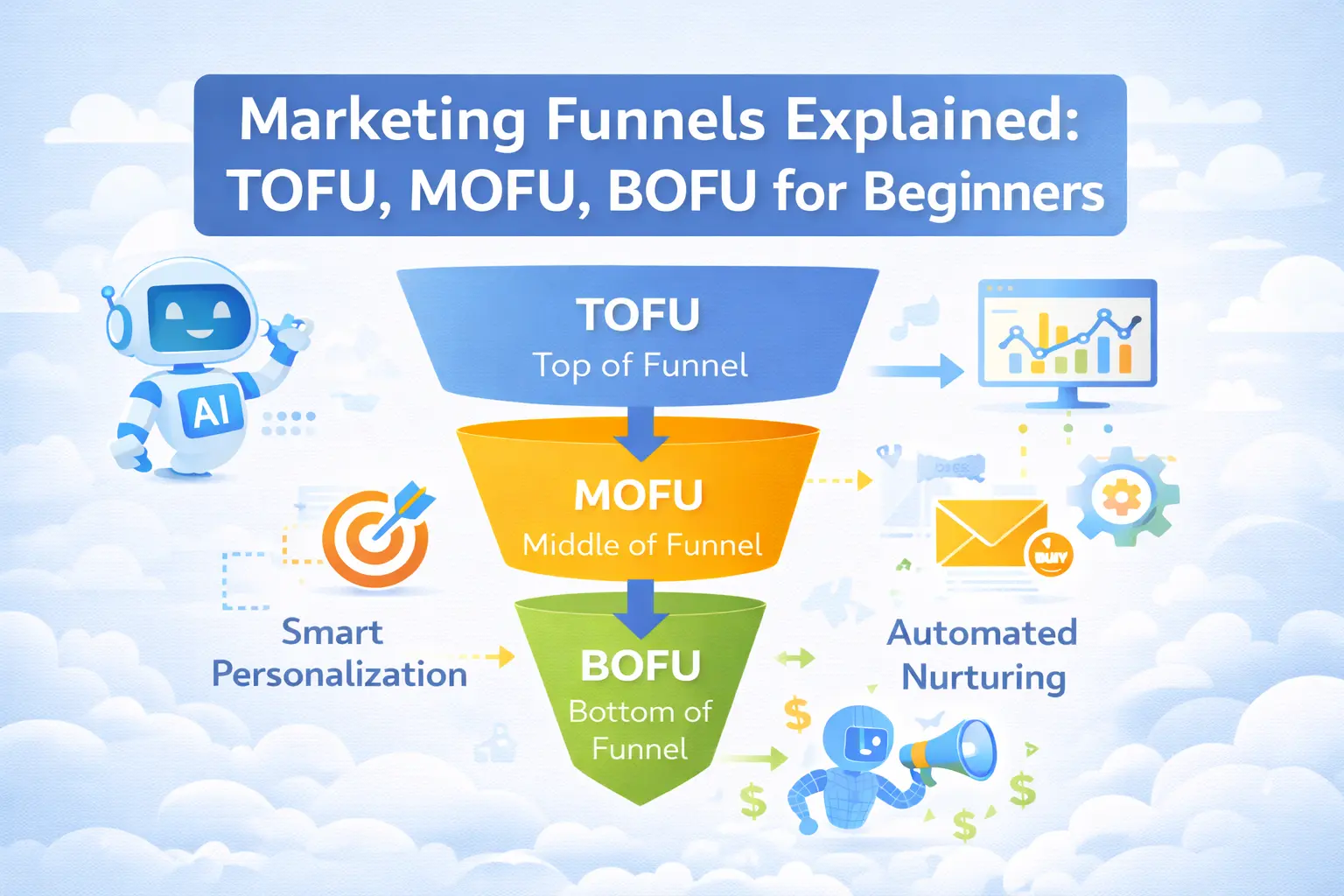
Introduction
What are principles of marketing?They are essential rules and guidelines that help businesses understand their customers, generate value, and communicate clearly, ensuring long-term growth. By adhering to these fundamentals, marketing becomes a strategic and reliable process. Conversely, neglecting them can lead even excellent products to fail. This difference explains why some brands succeed while others falter in the same marketplace.
Understanding marketing principles is more important than ever. Informed customers, fierce competition, and the rise of digital channels have changed how people find and trust brands. Companies that rely solely on promotions or trends may waste money, but those grounded in fundamental marketing principles can build stronger relationships and achieve steady success.
In this guide, you’ll learn what are principles of marketing in a practical, modern context. We’ll explore the 7 core principles of marketing, the classic 4Ps framework, and the influence of Philip Kotler, the father of modern marketing. You’ll also see how these foundations apply to inbound and digital marketing, where content, data, and customer experience drive sustainable growth.
Understanding Marketing Principles (Definition & Purpose)
At their core, marketing principles are the fundamental guidelines that dictate how a business connects its offerings with customer needs. When people ask, “what are principles of marketing?”, the most straight forward answer is that they are the bedrock concepts the immutable “rules of the game” that ensure an organization creates, communicates, and delivers value effectively. Unlike fleeting tactics that change with technology, these principles provide a stable foundation. The essential purpose of these concepts is to move an organization beyond mere “selling” and instead focus on building lasting relationships by deeply understanding consumer behaviour and solving their problems profitably.
Grasping these concepts is essential for a wide range of stakeholders. For students, perhaps studying for competitive events like principles of marketing DECA, these foundations provide the necessary theoretical framework for success. For entrepreneurs and corporate leaders, understanding the principles of marketing that every business should know is often the difference between a sustainable venture and one that struggles to gain traction. Renowned academic Philip Kotler, whose seminal texts define modern marketingeducation, emphasizes that these principles act as a compass in a complex business environment. Whether you are studying principles of marketing Philip Kotler style in a university setting or applying intersectional principles of business marketing and finance in a boardroom, the benefits are clear: better resource allocation, clearer brand messaging, and improved return on investment.
Finally, these guiding tenets act as the essential guardrails for strategic decision-making. They prevent businesses from chasing every new trend without a coherent plan. A solid grasp of the basic principles of marketing ensures that when a company shifts tactical execution, for instance, moving from traditional advertising to exploring what are fundamental principles of inbound and digital marketing the underlying strategy remains sound. They ensure that every digital campaign, product launch, and pricing strategy aligns squarely with the overarching goal of satisfying the target market’s needs.
Philip Kotler’s Principles of Marketing (Simplified)
Who Is Philip Kotler?

Philip Kotler is widely regarded as the father of modern marketing. His work transformed marketing from simple promotion into a customer-centric, strategy-driven discipline. When people ask what are principles of marketing are, much of the answer traces back to Kotler’s frameworks, which are used by businesses, universities, and even competitive programs like Principles of Marketing DECA.
His Core Ideas & Why They Still Matter
Kotler’s most significant contribution was shifting the focus from products to people. Instead of asking “How do we sell more?”, he taught marketers to ask, “Whose problem are we solving, and why should they care?” These ideas remain the principles of marketing that every business should know, especially in crowded digital markets.
At the heart of his thinking are the basic principles of marketing: customer value, differentiation, consistency, and long-term relationships. These principles underpin everything from brand positioning to pricing decisions and remain central to business marketing and finance, where marketing choices directly affect revenue, margins, and ROI. Even today, Kotler’s models guide discussions on the 7 principles of marketing and help simplify complex decisions into repeatable systems.
STP Explained: Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning
One of Kotler’s most influential frameworks is STP:
- Segmentation: Divide the market into clear groups based on needs, behaviour, or demographics.
- Targeting: Choose the most profitable and reachable segments to focus on.
- Positioning: Craft a clear message so customers instantly understand why your brand is different.
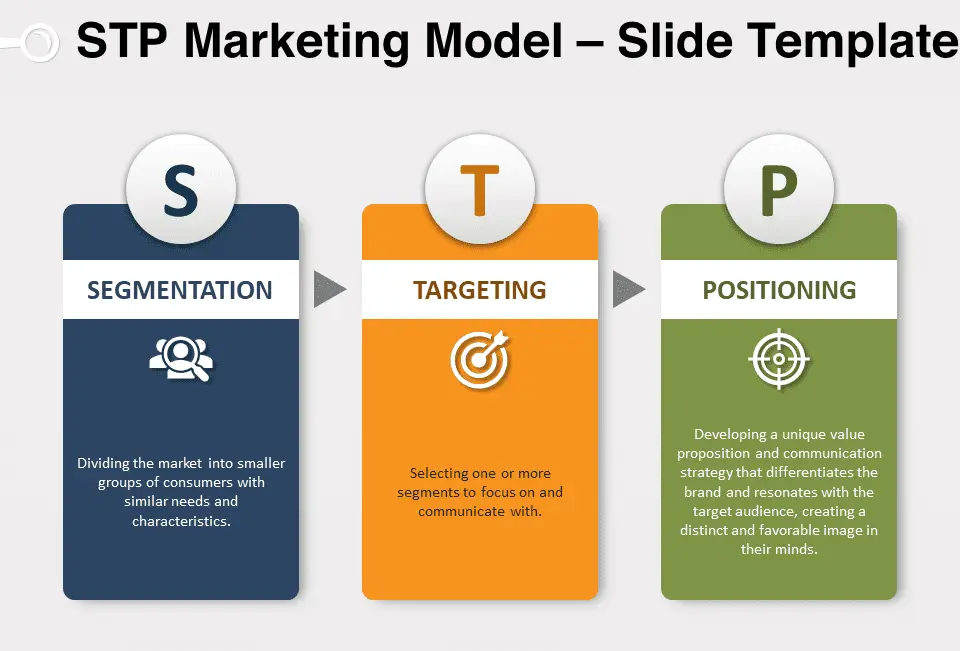
STP explains what are principles of marketing that inform action strategies before tactics. It also serves as a bridge between traditional theory and what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing, emphasizing the importance of understanding your audience through content, SEO, and personalization. This approach is reflected in the 7 core principles of marketing, which emphasize clarity and focus over broad, unfocused campaigns.
Academic & Practical Resources (PDF Reference)
For deeper study, many learners look for resources such as Philip Kotler’s Principles of Marketing PDF or Principles of Marketing by Philip Kotler PDF. While PDFs help with theory and exams, Kotler’s real value lies in applying these ideas in fundamental markets, whether you’re a student, a startup founder, or a marketing leader scaling growth.
The 7 Core Principles of Marketing (With Real Examples)
Understanding what are principles of marketing means knowing how successful brands generate value, remain relevant, and achieve consistent growth. These 7 core principles of marketing turn strategy into tangible results and are essential for any business, whether you’re a startup, a global corporation, or a student studying the principles of marketing DECA. Below, each principle is clearly explained with real-world examples from leading companies.
1) Customer Orientation / Value
Effective marketing begins with a focus on the customer. Brands succeed by thoroughly understanding their needs, pain points, and motivations, then providing value that directly addresses a problem. This concept forms the foundation of marketing principles and is central to Philip Kotler’s approach.
Example: Apple designs products around user experience, not features alone, turning customer value into loyalty.
2) Product Value
A product must deliver real value, not merely exist. Substantial value makes pricing easier, messaging clearer, and retention higher. This principle connects marketing decisions to principles of business marketing and finance, where perceived value drives margins and growth.
Example: Apple’s ecosystem (hardware + software + services) increases lifetime value, not just one-time sales.
3) Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP)
STP focuses marketing on the right audience with the right message. It’s essential for clarity and efficiency and foundational to the 7 principles of marketing frameworks and what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing, where personalization matters.
Example: Coca-Cola segments by lifestyle and occasion, targeting each group with distinct positioning (e.g., Coke Zero vs. classic).
4) Integrated Marketing / Value Proposition
All channels must tell one consistent story: product, price, place, and promotion working together. Integration strengthens the value proposition and reduces wasted spend.
Example: Coca-Cola aligns packaging, ads, social, and in-store presence to reinforce the same brand promise everywhere.
5) Relationship Building / Trust
Modern growth depends on trust and long-term relationships, not one-off transactions. This principle underpins loyalty, referrals, and brand equity, which are core principles of marketing in practice today.
Example: Amazon builds trust through reliable delivery, easy returns, and customer-first policies.
6) Communication, Branding & Promotion
Clear communication builds recognition and preference. Branding turns features into meaning; promotion amplifies that meaning across channels, especially in digital ecosystems.
Example: Amazon’s consistent tone across email, app, and ads reinforces reliability and convenience.
7) Continuous Improvement and Optimization
Markets change; winning brands test, learn, and optimize continuously. Data, feedback, and iteration keep strategies effective and crucial in inbound and digital contexts, as emphasized in principles of marketing philip kotler pdf resources for learners.
Example: Amazon relentlessly tests pricing, UX, and logistics to improve conversion and satisfaction.
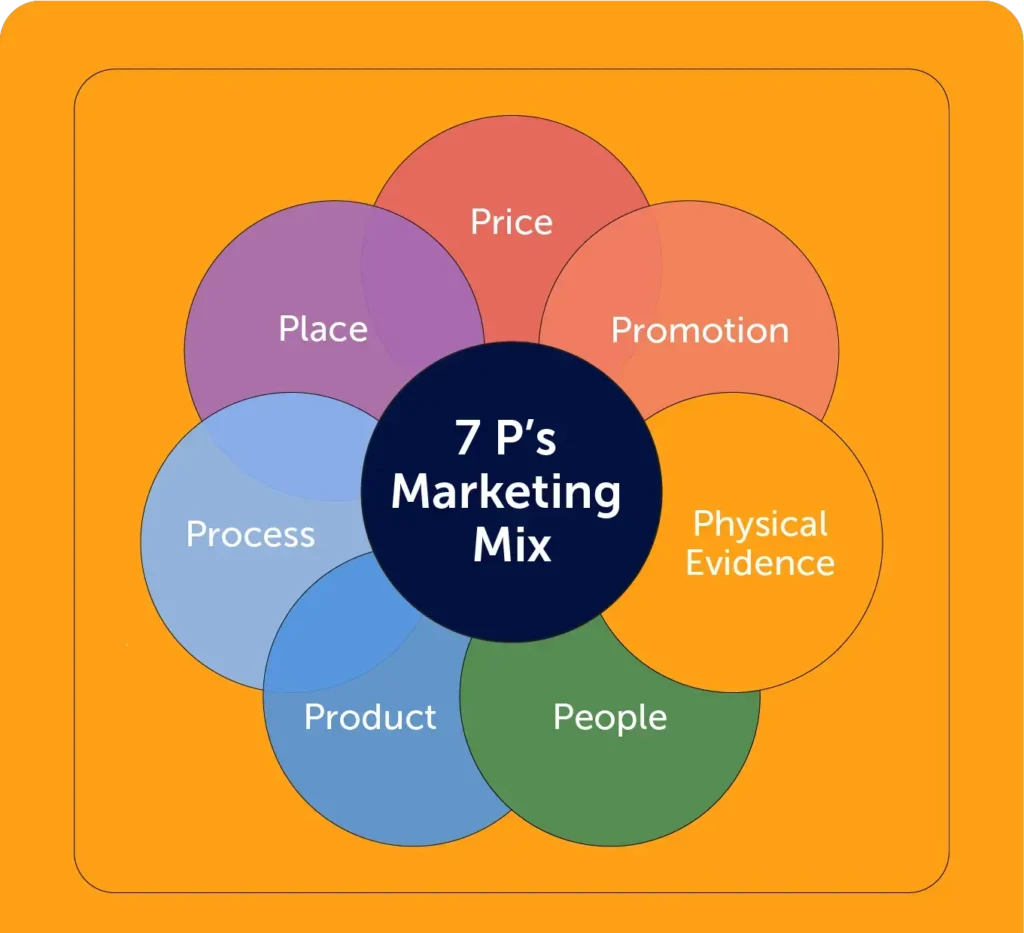
The 4Ps of Marketing – Classic Framework
To understand what are principles of marketing, you must understand the 4Ps of marketing, the classic framework that turns theory into execution. Introduced and popularized by Philip Kotler, the 4Ps help businesses design offers that match customer needs, market demand, and revenue goals. Even today, this framework remains one of the principles of marketing that every business should know because it connects strategy directly to action.
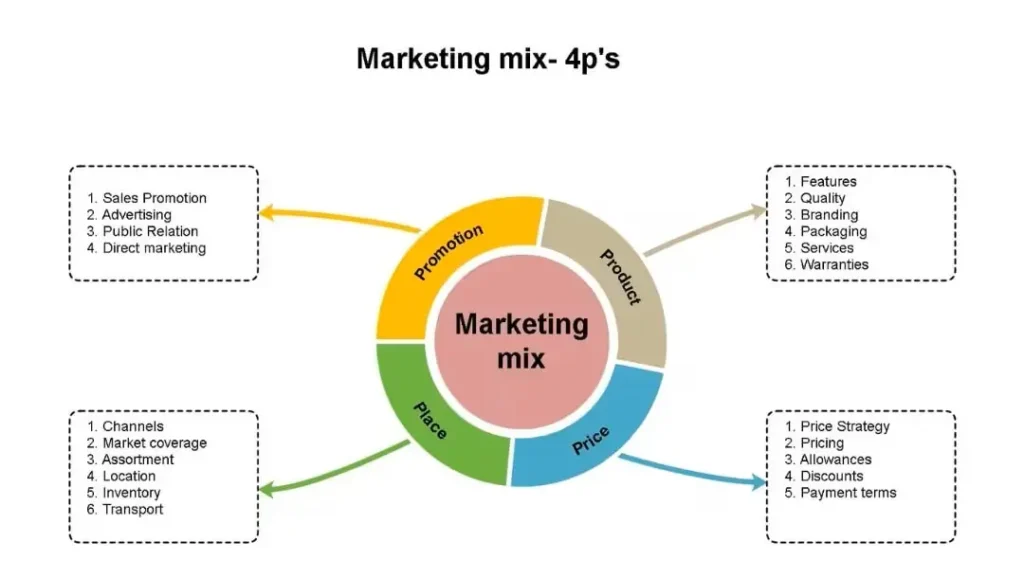
1) Product
The product is about solving a real customer problem, not just features. It includes quality, design, branding, and the overall experience. This aligns with the basic principles of marketing, where value creation comes before promotion.
Example:Apple doesn’t just sell devices; it sells simplicity, design, and ecosystem value, supporting both the 7 principles of marketing and long-term brand loyalty.
2) Price
Price reflects perceived value and directly impacts profitability, positioning, and demand. Smart pricing connects marketing decisions to principles of business marketing and finance, ensuring margins and growth stay aligned.
Example: Netflix uses tiered pricing to match different customer segments, an approach that reinforces the 7 core principles of marketing by balancing value and accessibility.
3) Place
Placeinvolves making the product accessible to customers whenever and wherever they want, whether online, offline, or both. In today’s markets, this also includes digital channels and logistics, tying closely to what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing.
Example: Amazon dominates through seamless distribution, fast delivery, and platform accessibility, turning convenience into a competitive advantage often studied in the principles of marketing DECA contexts.
4) Promotion
Promotioncovers how you communicate value through advertising, content, social media, email, and PR. Promotion works best when it’s consistent, customer-focused, and integrated across channels, ideas emphasized in the principles of marketing, Philip Kotler pdf learning resources.
Example: Coca-Cola maintains a unified global message across TV, digital, and in-store promotions, reinforcing brand recognition and trust.
How the 4Ps Connect to the 7 Principles
The 4Ps are not isolated tactics; they operationalize the 7 principles of marketing. Customer orientation drives Product decisions, value perception influences Price, STP informs Place, and integrated communication strengthens Promotion. Together, they form a system in which strategy guides execution. This connection is why the 4Ps continue to appear alongside Philip Kotler’s principles of marketing pdf materials in both academic and professional settings.
Modern Extensions of Marketing Principles
To fully understand what are principles of marketing, you also need to look beyond the classic 4Ps. As markets shifted toward services, experiences, and digital-first interactions, marketers added three powerful extensions: People, Process, and Physical Evidence. These extensions reinforce the principles of marketing that every business should know, especially in service-led and online environments.
People
People refer to everyone involved in delivering the brand experience: employees, partners, and even customers themselves. In service and digital businesses, people are the product. This idea is deeply rooted in the principles of marketing Philip Kotler, where customer-centricity and relationship value drive growth. Trained teams, consistent support, and brand-aligned behavior strengthen trust, as highlighted in the principles of marketing in DECA learning frameworks.
Process
The processis how the service or value is delivered from onboarding through support to fulfillment. Transparent, frictionless processes reduce confusion and increase satisfaction. In modern contexts, this aligns closely with what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing, where automation, personalization, and data guide smooth customer journeys. Well-designed processes also connect marketing decisions with principles of business marketing and finance, improving efficiency and ROI.
Physical Evidence
Physical Evidence includes everything customers see or experience that signals credibility, such as websites, apps, packaging, reviews, emails, and even UI design. While intangible, these cues heavily influence perception and trust. That’s why basic principles of marketing emphasize consistency across touchpoints, and why learners often reference Philip Kotler’s marketing principles to understand how evidence supports positioning.

How These Extensions Enhance the Traditional 4Ps
People, Process, and Physical Evidence don’t replace Product, Price, Place, and Promotion; they strengthen them. Together, they operationalize the 7 principles of marketing and 7 core principles of marketing, ensuring strategy translates into reliable experiences across channels. This integrated approach also addresses modern exam and practice needs found in Philip Kotler’s Principles of Marketing PDF resources.
What Are the Basic Principles of Inbound and Digital Marketing?
Understanding what are principles of marketing in today’s landscape requires a shift from interruption to attraction. Inbound and digital marketing are built on pull, not push, earning attention by delivering value at the right moment, on the right channel. This approach reflects the principles of marketing that every business should know, mainly as buyers research independently and expect relevance.
From Push → Pull Marketing.
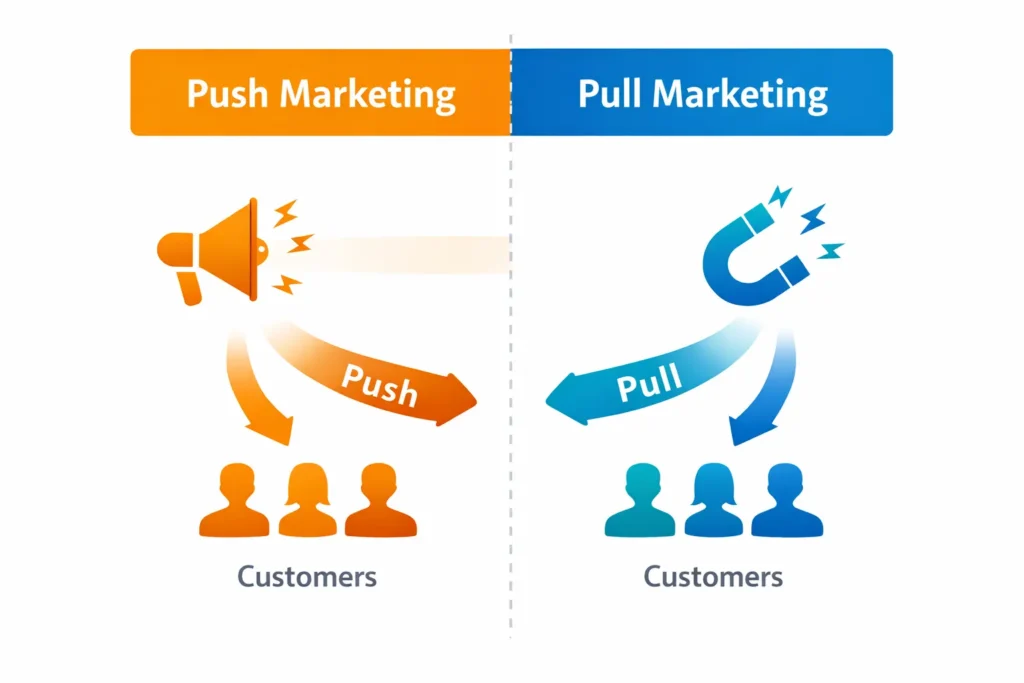
Traditional “push” tactics interrupt audiences with ads. Inbound flips this by attracting people through helpful content and experiences. This philosophy aligns with the principles of marketing by Philip Kotler, in which customer needs drive strategy rather than the other way around. It also connects marketing actions to principles of business marketing and finance by reducing wasted spend and improving ROI through intent-led acquisition.
The Role of Content
Content is the engine of inbound. Blogs, guides, videos, and case studies educate prospects and build trust before a sale. Done right, content supports the 7 principles of marketing by clarifying value, positioning, and differentiation often referenced in principles of marketing DECA frameworks for practical application.
SEO: Being Found When It Matters
SEO ensures your content appears when buyers are searching. Keyword intent, technical health, and on-page clarity turn visibility into qualified traffic. This is a cornerstone of what are fundamental principles of inbound and digital marketing, translating awareness into measurable growth.
Social Media: Distribution & Engagement
Social platforms amplify content and spark conversations. Consistent messaging across channels reinforces brand trust, one of the 7 core principles of marketing, and keeps audiences engaged throughout the journey.
Email Automation: Nurture at Scale
Email automation delivers the right message at the right time for onboarding, education, offers, and retention. These workflows embody basic principles of marketing by aligning relevance, timing, and value. Many learners deepen their understanding of theory through resources on the principles of marketing by Philip Kotler, but automation is where theory meets execution.
Principles of Marketing for DECA Students
Understanding what are principles of marketing is a core requirement for students preparing for competitive business programs like DECA. DECA doesn’t test memorization alone; it evaluates how well students can apply marketing fundamentals to real business scenarios. That’s why mastering the principles of marketing that every business should know gives DECA students a clear advantage in exams, role-plays, and written events.
DECA Standards & Competitive Events
DECA frameworks are built on real-world marketing logic. Events such as Marketing Management, Entrepreneurship, and Integrated Marketing Campaigns expect students to apply basic principles of marketing, customer focus, value creation, segmentation, and promotion under time pressure. These same foundations appear in the 7 principles of marketing models and are closely aligned with Philip Kotler’s principles of marketing, which many curricula reference conceptually.
Key Points for Students and Professionals
For students, marketing principles provide structure: they help you quickly analyze a case, identify the target market, and recommend actions that make business sense. For professionals, the same principles connect marketing decisions to outcomes, reflecting principles of business marketing and finance such as pricing logic, ROI, and customer lifetime value. This overlap is why DECA-style thinking translates well to real careers and even to modern practices, such as the basic principles of inbound and digital marketing, where strategy must be clear before execution.
Exam-Friendly Bullet Summary (Quick Revision)
- Customer First: Always identify needs before tactics
- Value Proposition: Explain why the customer should choose the product
- STP: Segment, target, and position clearly
- Marketing Mix: Apply Product, Price, Place, Promotion logically
- Consistency: Align message, channel, and experience
- Measurement: Tie actions to results (sales, awareness, ROI)
Many students deepen their understanding of theory using resources like Philip Kotler’s Principles of Marketing, but DECA success comes from applying these ideas quickly and clearly, not by quoting textbooks. When you ground your answers in the 7 core principles of marketing, judges see strategic thinking, not guesswork.
How Marketing Principles Drive Business & Financial Success
Understanding what are principles of marketing isn’t just about branding it’s about building predictable revenue and protecting profit. When teams apply the principles of marketing that every business should know, marketing stops being a cost center. It becomes a growth engine aligned with principles of business marketing and finance.
Linking Marketing to Revenue & ROI
Strong marketing principles connect demand creation to measurable outcomes. Precise positioning, focused targeting, and consistent messaging increase conversion rates and reduce wasted spend. Core ideas emphasized in the principles of marketing, Philip Kotler. In modern environments, this alignment extends to what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing, where intent-led channels (content, SEO, email) compound ROI by attracting qualified buyers over time. The result: lower acquisition costs, higher conversion rates, and defensible margins, often summarized in the 7 principles of marketing.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
One-off sales don’t drive financial success; lifetime relationships drive it. Marketing principles prioritize retention, trust, and value delivery, multiplying CLV through repeat purchases and referrals. This logic underpins 7 core principles of marketing and is reinforced in basic principles of marketing curricula and principles of marketing DECA case analysis. When CLV rises, revenue becomes more stable, and forecasting improves, both of which are critical for finance planning.
Budgeting for Campaigns (Spend with Intent)
Principled marketing turns budgeting into strategy. Instead of spreading spend thin, budgets are allocated by audience value, funnel stage, and expected return, linking execution to principles of business marketing and finance. Inbound-led programs further improve efficiency by investing upfront in assets that pay back over time. Many teams study theory via principles of marketing philip kotler pdf resources, but the real win comes from applying those principles to budget decisions that scale profitably.
Practical Examples of Marketing Principles in Action
Seeing what are principles of marketing at work is easiest through authentic brands that apply fundamentals consistently. The cases below illustrate the principles of marketing that every business should know, from value creation to integration and optimizationexecuted at scale, tied to outcomes that finance teams care about.
Example 1: Apple’s Customer-Centric Approach
Apple wins by obsessing over customer value before tactics. Product design, pricing tiers, retail experience, and after-sales support are aligned to a single promise: simplicity and delight. This mirrors the principles of marketing: Philip Kotler starts with customer needs, then builds the offer. Apple’s ecosystem thinking also reflects the basic principles of marketing taught in classrooms and competitive settings, like the principles of marketing DECA.
Why it works: Clear positioning reduces friction, increases loyalty, and raises lifetime value outcomes that reinforce principles of business marketing and finance.
Example 2: Coca-Cola’s Integrated Campaigns
Coca-Cola demonstrates integration across channels. From TV to social to in-store, messaging stays consistent while creative adapts locally. This alignment is a hallmark of the 7 principles of marketing, ensuring the brand story is unmistakable everywhere. It also shows how integration supports what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing by combining reach with engagement.
Why it works: Consistency compounds recall and trust, driving efficient spend and predictable returns ideas reinforced in principles of marketing philip kotler pdf resources.
Example 3: Amazon’s Innovation & Optimization
Amazon operationalizes continuous improvement testing UX, logistics, pricing, and recommendations relentlessly. Data-led optimization brings the 7 core principles of marketing to life, linking experience to conversion and retention. Amazon’s flywheel model is often cited alongside Philip Kotler’s principles of marketing and PDF discussions on turning insights into scalable execution.
Why it works: Faster learning cycles lower costs, increase CLV, and strengthen margins through precise alignment with principles of business marketing and finance.
Common Marketing Mistakes to Avoid
Knowing what are principles of marketing is only half the job avoiding the mistakes that undermine them is what protects growth. Many teams invest in tools and campaigns but ignore the principles of marketing that every business should know, creating gaps between strategy, execution, and results. Below are the most common pitfalls and how to fix them.
1) Ignoring Customer Feedback
When brands stop listening, relevance drops. Reviews, surveys, support tickets, and on-site behavior reveal what customers value and where friction lives. Ignoring feedback breaks the basic principles of marketing, which prioritize customer value and continuous improvement. Modern teams close the loop using insights from content, SEO, and email practices aligned with what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing.
Fix: Build a simple feedback loop (collect → analyze → act → communicate).
2) Product-First Mindset
Leading with features instead of problems is a classic error. Product-first messaging assumes customers will “figure it out,” while principle-led marketing starts with needs, outcomes, and differentiation. This shift is central to the principles of marketing, Philip Kotler, and it’s reinforced in learning frameworks like the principles of marketing DECA.
Fix: Reframe every message around the customer’s job-to-be-done and value proposition.
3) Focusing Only on Sales, Not Relationships
Short-term promotions can spike revenue, but they rarely build loyalty. Sustainable growth comes from trust, retention, and lifetime value ideas embedded in the 7 principles of marketing and the 7 core principles of marketing. Relationship-first thinking also improves forecasting and margins, supporting principles of business marketing and finance.
Fix: Invest in retention (email nurturing, community, post-purchase care) alongside acquisition.
4) Inconsistent Messaging
Mixed messages across ads, the website, social media, and email confuse buyers and weaken brand equity. Consistency is a non-negotiable principle taught across basic principles of marketing curricula and referenced in principles of marketing philip kotler pdf resources.
Fix: Create a clear brand message map and enforce it across channels and teams.
Tools to Apply Marketing Principles
Understanding what are principles of marketing becomes powerful only when you can apply them consistently. Tools turn theory into execution, helping teams operationalize the principles of marketing that every business should know across channels, journeys, and budgets. Below are the core tool categories that translate principles into measurable outcomes.
Marketing Automation
Automation enables relevance at scale, sending the right message to the right person at the right time. From lead nurturing to onboarding and retention, workflows support customer-centricity and relationship-building, central to the principles of marketing Philip Kotler and reinforced in basic marketing curricula. Automation also embodies what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing by aligning content, timing, and intent.
Use it for: Lead scoring, drip emails, lifecycle messaging, and re-engagement.
Analytics & Customer Insights
Analytics connect actions to outcomes. Dashboards reveal who converts, why they churn, and where value compounds, critical for aligning marketing with principles of business marketing and finance. Insight-led decisions support optimization, one of the 7 principles of marketing, and are frequently emphasized in case analysis, such as the principles of marketing DECA.
Use it for: Funnel analysis, cohort tracking, CLV, and ROI attribution.
Social Media & Content Strategies
Content educates, social distributes, and community engages. Together, they operationalize trust, consistency, and positioning core ideas in 7 core principles of marketing and often explored through theory sources such as principles of marketing philip kotler pdf. Strong strategies keep messaging aligned across touchpoints and convert attention into demand.
Use it for: Thought leadership, demand generation, community building, and brand consistency.
Measuring the Impact of Marketing Principles
Understanding what are principles of marketing is only valuable if you can measure whether they’re working. Measurement is where strategy meets accountability. When brands track the right signals, they turn the principles of marketing that every business should know into repeatable growth, especially across modern, data-driven environments.
KPIs & Metrics (What to Track)
Key Performance Indicators translate principles into numbers. Metrics such as traffic quality, engagement rate, lead-to-customer conversion rate, and customer acquisition cost indicate whether value creation and positioning are resonating with customers. These measurements reinforce basic principles of marketing by keeping teams focused on outcomes, not activity. In practice, many learning frameworks, including principles of marketing DECA stress KPI selection as a core analysis skill
Track: Qualified traffic, conversion rate, CAC, CLV, engagement depth.
ROI & Conversion Tracking (What Pays Off)
ROI answers the finance question: Is marketing profitable? By connecting campaigns to revenue, teams align execution with principles of business marketing and finance. Conversion tracking across funnels ads, content, email also reflects what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing, where intent-led journeys compound returns over time. These ideas are consistently reinforced in Philip Kotler’s principles of marketing, which emphasize accountability and long-term value.
Track: Revenue attribution, funnel drop-offs, cost per conversion, payback period.

Customer Satisfaction & Retention (What Lasts)
Retention proves whether principles are creating trust. Satisfaction scores, repeat purchase rate, and churn indicate whether promises match experience, which is core to the 7 principles of marketingand the 7 core principles of marketing. While theory is often studied through marketing principles (e.g., Kotler), retention metrics show whether those principles are actually embedded in operations.
Track: NPS/CSAT, retention rate, repeat purchase frequency, churn.
How Small Businesses Can Leverage Marketing Principles
For small businesses, understanding what are principles of marketing is the fastest way to grow without wasting budget. Principles turn limited resources into focused action, helping owners apply the principles of marketing that every business should know with discipline, clarity, and measurable impact.
Budget-Friendly Strategies (Do More with Less)
Small budgets win when strategy leads tactics. Start with precise positioning, a narrow target audience, and a simple value proposition, foundations emphasized in the principles of marketing,Philip Kotler. Prioritize channels that compound over time (content, SEO, email) to align with what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing. This approach reduces paid spend, improves intent, and connects effort to outcomes, which are key to principles of business marketing and finance.
Action ideas:
- Publish one helpful blog per week (answer real customer questions).
- Build an email list and automate basic nurture.
- Retarget warm visitors instead of broad ads.
Building Brand Loyalty (Retain to Grow)
Growth isn’t just acquisition; it’s retention. Loyalty increases lifetime value and stabilizes cash flow outcomes rooted in basic principles of marketing and often taught through the 7 principles of marketing frameworks. Consistent service, clear messaging, and post-purchase care transform buyers into advocates, concepts reinforced by the principles of marketing in DECA case thinking.
Action ideas:
- Create a simple loyalty or referral offer.
- Send value-first emails (tips, updates, thank-you notes).
- Collect and act on reviews to build trust.
Local & Digital Marketing Tactics (Win Where You Compete)
Local visibility plus digital reach is a potent mix. Optimize locallistings, publish geo-specific content, and engage your community on social. Pair this with inbound tactics to capture intent, practical applications of what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing that also reflect the 7 core principles of marketing (focus, consistency, optimization). Many owners study marketing theory through the principles of Philip Kotler, but results come from applying it locally.
Action ideas:
- Optimize Google Business Profile and local SEO pages.
- Post short, helpful videos answering FAQs.
- Run small, targeted offers to nearby audiences.
The Future of Marketing Principles
To understand what are principles of marketing in the years ahead, we have to look at how technology, data, and values are reshaping customer expectations. While the foundations remain timeless, the way brands apply them is evolving fast. This shift reinforces the principles of marketing that every business should know, especially as markets become more competitive and transparent.
AI & Personalization (From Mass to Individual)
Artificial intelligence is transforming how brands create relevance at scale. AI-driven personalization tailors content, offers, and timing to individual behavior, turning customer focus into a measurable advantage. This evolution aligns closely with the principles of marketing by Philip Kotler, where understanding customer needs precedes tactics, and it operationalizes the basic principles of inbound and digital marketing by attracting, engaging, and converting based on intent rather than interruption.
What this means: Better experiences, higher conversion rates, and stronger loyalty without increasing spend.
Data-Driven Decision-Making (Evidence Over Opinion)
Future-ready marketing replaces assumptions with evidence. Real-time analytics, experimentation, and attribution models ensure decisions connect directly to outcomes, core to principles of business marketing and finance. This approach also strengthens the basic principles of marketing by keeping strategies focused on value creation and optimization, a theme reinforced across the 7 principles of marketing and the 7 core principles of marketing discussions.
What this means: Faster learning cycles, clearer ROI, and predictable growth.
Sustainability & Ethical Marketing (Trust as a Differentiator)
Consumers increasingly reward brands that act responsibly. Sustainability, privacy, and ethical messaging are no longer optional; they’re signals of trust. These priorities echo long-standing teachings found in principles of marketing DECA frameworks and academic resources like principles of marketing philip kotler pdf, where long-term relationships matter more than short-term gains.
What this means: Brands that align values with actions build resilience and preference over time.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implement Marketing Principles
Implementing what are principles of marketing are doesn’t require a big team or budget; it requires a transparent, repeatable process. The steps below translate the principles of marketing that every business should know into action, while staying aligned with modern practices and measurable outcomes.
Step 1: Research Your Audience
Start with evidence, not assumptions. Identify who your best customers are, what problems they’re trying to solve, and how they decide. Use interviews, reviews, analytics, and search intent to map needs and triggers. This customer-first approach reflects principles of marketing philip kotler and is foundational to what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing, where relevance drives results.
Checklist: personas, pain points, buying stages, objections.
Step 2: Define Your Value Proposition
Turn insights into a clear promise: why choose you? A strong value proposition clarifies benefits, differentiators, and proof. This step anchors the basic principles of marketing and supports financial outcomes tied to principles of business marketing and finance by improving conversion and pricing power.
Checklist: primary benefit, differentiation, proof (reviews, results).
Step 3: Align Messaging & Channels
Consistency builds trust. Align your message across website, ads, social, email, and sales conversations so customers hear one story. This alignment operationalizes the 7 principles of marketing and 7 core principles of marketing, ensuring each channel reinforces the same value.
Checklist: message map, channel roles, cadence, brand voice.
Step 4: Monitor, Test, and Optimize
Measure what matters, test improvements, and iterate. Track KPIs, run A/B tests, and refine based on data habits emphasized in case analyses, such as the principles of marketing DECA, and reinforced through academic references, such as Philip Kotler’s Principles of Marketing (PDF).
Checklist: KPIs, experiments, insights, and following actions.
Conclusion
Marketing success isn’t about chasing tactics; it’s about mastering the fundamentals. In this guide, we covered what are principles of marketing through the lenses that matter most today: the 7 core principles of marketing, the classic 4Ps framework, the customer-first thinking popularized by Kotler, and the modern shift to inbound and digital marketing. Together, these foundations show how strategy leads execution and how execution leads results.
For businesses, these principles translate into more precise positioning, smarter budgets, more substantial ROI, and long-term growth. They connect marketingdecisions directly to revenue, retention, and brand trust. For students, especially those preparing for exams and case-based programs, these same ideas provide a reliable framework for analyzing problems, recommending solutions, and performing confidently in real-world scenarios.
Whether you’re building a brand, scaling a company, or studying marketing fundamentals, the takeaway is simple: principles don’t change; how you apply them does. Focus on customer value, align your mix, measure what matters, and keep optimizing. Do that consistently, and marketing stops being guesswork and starts becoming a predictable engine for growth.
FAQs – What Are Principles of Marketing?
1) What are the 7 principles of marketing?
The 7 principles of marketing focus on creating value and driving sustainable growth. They typically include customer orientation, product value, segmentation–targeting–positioning (STP), integrated marketing, relationship building, communication & branding, and continuous improvement. Together, these 7 core principles of marketing help businesses move from tactics to strategy.
2) How can small businesses apply these principles?
Small businesses can apply marketing principles by narrowing their audience, clarifying a strong value proposition, and choosing a few high-impact channels. Start with customer research, align messaging across touchpoints, and measure results. This practical approach reflects the principles of marketing that every business should know, especially when budgets are limited.
3) Are the 4Ps still relevant today?
Yes. The 4Ps (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) remain foundational. However, they work best when extended with People, Process, and Physical Evidence, especially in services and online experiences. This evolution aligns with principles of marketing Philip Kotler, where classic frameworks adapt to modern markets.
4) How do marketing principles affect ROI?
Marketing principles improve ROI by focusing spending on the right audience, message, and channels. Precise positioning and consistent execution increase conversion rates and customer lifetime value, directly supporting principles of business marketing and finance through predictable, profitable growth.
5) Can digital marketing change traditional principles?
Digital marketing doesn’t replace traditional principles; it amplifies them. Data, automation, and personalization make customer-centricity and optimization easier to execute. This is why what are basic principles of inbound and digital marketing still map back to the same core foundations.
6) Is inbound marketing part of digital marketing?
Yes. Inbound marketing is a subset of digital marketing focused on attracting customers through valuable content, SEO, social media, and email rather than interruption. It applies timeless principles like trust and value creation in a modern, scalable way.